Sugar beet vs sugar cane: Best uses in food industries
Wiki Article
All About Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane: Which One Offers Greater Benefits and Makes Use Of?
The contrast between sugar beet and sugar cane provides a nuanced exploration of their corresponding advantages and applications. Each crop has distinctive nutritional accounts and expanding problems that influence their usage in numerous sectors. As consumer choices change towards much healthier alternatives, the relevance of these two resources of sugar comes to be increasingly substantial. Comprehending their distinctions might reveal understandings right into which might ultimately serve far better in a changing market landscape. What elements will shape this recurring discussion?Summary of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane
Sugar beet and sugar cane are two main sources of sugar, each with distinctive attributes and benefits. Sugar beet, a root plant mainly grown in pleasant environments, is recognized for its high sucrose content, which can vary from 15% to 20%. This crop is commonly refined right into granulated sugar, molasses, and other by-products. Its farming permits a much shorter expanding season and less dependence on exotic environments.On the other hand, sugar cane flourishes in warmer, tropical areas and is typically concerned for its coarse stalks, which can produce 10% to 15% sucrose. The handling of sugar cane not just generates sugar however likewise causes products like rum and ethanol, making it versatile. Both plants add considerably to the international sugar market, with their special expanding problems and processing approaches influencing their agricultural and financial relevance. Ultimately, the choice in between sugar beet and sugar cane frequently depends upon local environments and market needs.
Nutritional Profiles: Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane
The nutritional accounts of sugar beet and sugar cane reveal significant differences in their nutrient make-ups. Sugar beet often tends to provide a higher focus of nutrients, while sugar cane mainly supplies power in the type of carbohydrates. Additionally, the glycemic index of these two sources differs, affecting their impacts on blood sugar level degrees.Nutrient Structure Contrast
When comparing the nutrient structure of sugar beet and sugar cane, distinctive distinctions arise that can affect nutritional selections. Sugar beetroots are understood for their higher fiber content, supplying roughly 2 grams of fiber per 100 grams, while sugar cane has marginal fiber (Sugar beet vs sugar cane). Concerning vitamins, sugar beetroots offer a variety of B vitamins, particularly folate, which supports cellular health, whereas sugar cane includes less vitamins generally. In addition, sugar beetroots boast a higher mineral material, including potassium and magnesium, important for numerous physical features. Sugar cane mostly supplies carbohydrates, specifically sucrose, but does not have the nutrient thickness found in sugar beets. These differences highlight the dietary advantages of sugar beets contrasted to sugar cane in a well balanced diet regimen
Glycemic Index Differences
Just how do sugar beets and sugar cane differ in their glycemic index, and what effects does this have for individuals monitoring their blood sugar degrees? Sugar beets usually have a reduced glycemic index (GI) contrasted to sugar cane, which suggests they trigger a slower and more progressive boost in blood sugar levels. This difference is particularly essential for people with diabetes or those concerned regarding blood glucose monitoring. A lower GI food can aid keep steadier power degrees and minimize the threat of insulin spikes. While both resources are mainly composed of sucrose, the varying fiber and nutrient material in sugar beetroots might add to their reduced GI, making them a possibly far better alternative for health-conscious consumers.Growing Problems and Geographic Circulation
Both sugar beet and sugar cane offer as crucial resources of sugar, their expanding conditions and geographical circulation vary substantially. Sugar cane grows in tropical and subtropical environments, needing cozy temperature levels, plentiful sunshine, and substantial rainfall. It is mainly cultivated in nations such as Brazil, India, and China, where these ecological aspects are excellent. Sugar beet vs sugar cane. In comparison, sugar beet likes warm climates, thriving in cooler regions with well-drained dirt. Significant producers of sugar beet include the United States, Russia, and numerous European countries, where the expanding season aligns with cooler temperaturesThe differences in climate needs lead to varying growing practices; sugar cane is typically grown as a seasonal crop, while sugar beet is generally grown each year. This geographical difference not only affects regional agricultural economies yet likewise shapes view it neighborhood techniques associated with sugar manufacturing and processing. Comprehending these elements is vital for examining the benefits and applications of each source.
Ecological Impact of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Manufacturing
While both sugar beet and sugar cane contribute greatly to international sugar production, their ecological influences differ read the full info here substantially. Sugar cane cultivation often requires large areas of land and water, resulting in deforestation and environment loss in some regions. Furthermore, making use of fertilizers and chemicals in sugar cane farming can result in dirt deterioration and water air pollution. On the other hand, sugar beet is typically grown in cooler environments and requires less water, which might decrease the pressure on local water resources. Extensive farming techniques associated with sugar beet can also lead to soil erosion and nutrient depletion. The processing of both plants produces waste, yet sugar cane has a higher possibility for spin-offs, such as bioenergy, which can mitigate some environmental influences. Ultimately, the sustainability of each plant largely depends on farming techniques and local management methods employed throughout the manufacturing cycle.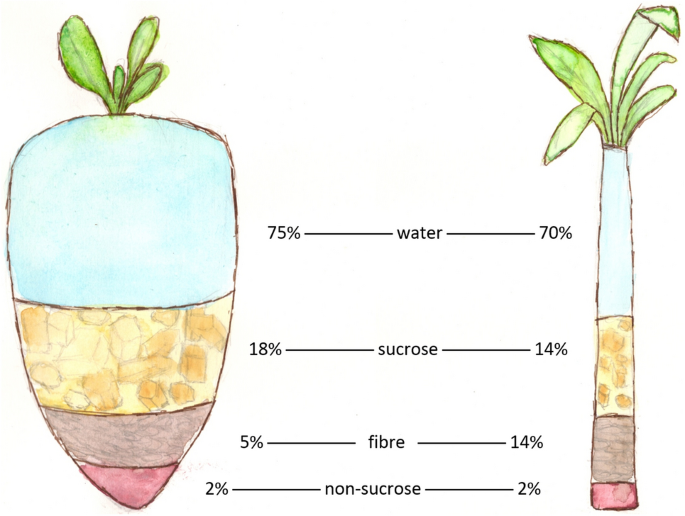
Handling Methods and Efficiency
Processing techniques for sugar beet and sugar cane vary markedly, impacting general performance and yield. Sugar beets undergo a procedure that includes washing, slicing, and drawing out juice with diffusion or pushing. The juice is then cleansed, focused, and taken shape, resulting in granulated sugar. This method is normally effective, with a high sugar extraction rate.On the other hand, sugar cane handling entails squashing the cane to remove juice, complied with by clarification and evaporation. The juice is then boiled to produce sugar crystals. While both approaches work, sugar cane handling can be a lot more labor-intensive and lengthy because of the larger range of procedures and the requirement for much more substantial equipment.
Sugar beet processing typically results in a higher sugar web content per ton contrasted to sugar cane, making it a much more efficient alternative in certain regions. Generally, the selection of handling approach affects not just the return but also the economic practicality of sugar manufacturing.
Applications in the Food Market
In the food industry, sugar beet and sugar cane offer distinctive roles in sugar production. Each source uses unique features that influence their cooking applications, from baked products to drinks. Understanding these differences can assist manufacturers and cooks in selecting one of the most ideal ingredient for visit their website their requirements.Sweetener Production Differences
Although both sugar beet and sugar cane serve as essential resources for sweetener production, their applications in the food sector differ significantly. Sugar cane is mainly connected with producing raw sugar and molasses, which are extensively used in beverages, confections, and baked products. Its juice is also fermented to produce rum. Conversely, sugar beet is mostly processed right into polished sugar, which is preferred in the production of granulated sugar and different other sugar. The extraction procedure for sugar beet is much more simple, permitting higher yields of white sugar. Additionally, sugar beet's convenience enables the development of alternative sugar, such as beet syrup. These distinctions highlight the distinct functions each resource plays in meeting the diverse requirements of the food market.Culinary Uses Contrast
Cooking applications of sugar beet and sugar cane expose unique choices amongst chefs and food suppliers. Sugar cane, frequently regarded as the traditional sweetener, is favored in a selection of products, including syrups, molasses, and beverages like rum. Its natural flavor matches treats, marinades, and sauces. Alternatively, sugar beet, used mostly in granulated sugar form, is regularly integrated right into baked products, candies, and processed foods. Its neutral taste profile allows it to blend perfectly into various dishes. Additionally, sugar beet is acquiring traction in organic and non-GMO markets, interesting health-conscious customers. Ultimately, the choice in between sugar beet and sugar cane rests on details cooking applications, flavor choices, and market trends within the food industry.Wellness Considerations and Consumer Preferences
A growing variety of consumers are significantly knowledgeable about the wellness ramifications related to sugar resources, resulting in a keen passion in the advantages of sugar beet versus sugar cane. Both sugar sources have distinct dietary accounts that may affect consumer selections. Sugar beets often tend to contain slightly extra fiber and important nutrients, which can interest health-conscious individuals. Conversely, sugar cane is commonly viewed as a more all-natural and much less refined option, potentially bring in those seeking organic or raw items.The increasing appeal of different sweeteners has triggered consumers to inspect traditional sugars extra carefully (Sugar beet vs sugar cane). Awareness of extreme sugar consumption's health risks, such as weight problems and diabetic issues, has fueled a demand for openness relating to the beginnings and handling methods of sweeteners. Eventually, private choices remain to form the debate in between sugar beet and sugar cane, showing a more comprehensive pattern in the direction of much healthier consuming routines and educated consumerism
Frequently Asked Concerns
What Are the Historic Uses Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
Historically, sugar beet and sugar cane have actually functioned as key sources of sugar. Sugar cane, cultivated for centuries in tropical regions, offered sugar, while sugar beet emerged in Europe throughout the 18th century, enhancing regional sugar manufacturing.

Just How Do Sugar Beet and Cane Affect Citizen Economies?
Sugar beet and sugar cane significantly influence neighborhood economic climates through job development, agricultural productivity, and profession. Their growing promotes country development, sustains regional services, and generates tax obligation profits, inevitably enhancing area sustainability and economic durability.Are There Any Social Value Distinctions Between Sugar Beet and Cane?
Cultural value ranges sugar beet and sugar cane. Sugar cane frequently stands for tropical heritage and conventional practices, while sugar beet is connected with farming advancement and industrialization, reflecting different regional identifications and historic contexts in their manufacturing.What Are the Main Vermin Affecting Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
The main parasites affecting sugar beet consist of aphids and root maggots, while sugar cane encounters risks from borers and planthoppers. Both crops need mindful administration to minimize damage and assurance healthy and balanced yields.Just How Do Climate Modifications Impact Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Growing?
Environment changes substantially affect sugar beet and sugar cane growing by modifying development conditions, shifting bug populaces, and impacting water accessibility. These variables can reduce yields and impact total agricultural sustainability in affected regions.Report this wiki page